
Viz Mosart User Guide
Version 4.1 | Published July 09, 2021 ©
Templates
Some template features are introduced below:
Introduction
A Viz Mosart template is the key element of controlling external devices handled by Viz Mosart. It enables the sending of studio control commands to multiple devices, simultaneously.
Typically, the actions defined on the template are initiated either:
-
Automatically
Either invoked from another template or at a given time as part of the rundown -
Preconfigured
Configured in the newsroom control system (NRCS or NCS) as part of a rundown, and then manually executed by the Viz Mosart operator -
Manually
The operator initiates the template-driven operation, usually with a keyboard shortcut or touch panel.
Template Sets
The templates are organized in template sets. Typically, there will be one template set for each show/program. When Mosart is running, one template set will be current, meaning that templates to be executed are drawn from this set. The operator may easily select another set to be the new current set. (For more information, see Current template set in Definitions below.)
In addition to these per-show template sets, there is a special template set Directtakes. The templates in this set are not meant to be executed as part of the rundown (as are other templates). Rather, they are normally executed immediately in an ad-hoc fashion, e.g. by the operator entering its number on the numeric keypad. The templates in this set are called direct take templates.
Standalone
Traditionally, Viz Mosart template sets are treated individually, with no connection to each other.
For example, a template set is created for each show or program. This is usually combined with automatically selecting the template set through the associated NCS rundown. In addition, startup commands for preparing the studio (lights, sound etc) for running the show are included in the template set.
When creating a template set for a new program, it is based upon a copy of an existing template set, with small adjustments according to the functionality needed by the program.
When this new template set is created (by copying an existing set), a copy of all templates is made, and no references are made between the original and copied templates. Each template set is classified as ‘standalone’.
Disadvantages with this approach:
-
Many duplicates are created. Normally only a few of the templates in the set need to be adjusted for meeting the needs of a new program.
-
With an ever-growing bank of templates being created for each new show, the amount of stored templates in Viz Mosart can exceed system norms. This results in long response times when saving templates and increases the memory footprint of both the Mosart Server and Viz Mosart client workstations.
-
Maintenance of templates becomes cumbersome and error prone. When a change is made in a template that is common for all template sets, the same change has to be applied individually to every template set. This is a time consuming task across numerous template sets.
Hierarchical
An alternative approach to standalone is hierarchical template sets. This method also enables a new template set to be created, based on the logic of an existing template set. However, to begin with, no templates are copied from the existing template set.
Only when a change is made to an existing template, or when a new template created, is a template created and stored in the new template set.
The hierarchical approach can be adopted with all existing (standalone) template sets, to optimize machine capacity and introduce a more efficient workflow.
Referring to the background discussion in Working with Template Sets above, when you copy a template set, it is more efficient to use a hierarchical approach. These operations are usually performed by a system administrator, as outlined in Creating Hierarchic Template Sets below.
Working with Templates
The Template Editor, from where individual templates and template sets (standalone and hierarchic) can be created and edited, is accessed from the AV Automation application.
-
To browse templates, navigate to Main menu > Devices > Template editor.

Templates displayed in Template Editor provide detailed information of their origin, function and configuration.
With a combination of mouse-over and contextual menus, an administrator can create and modify the templates that comprise a Viz mosart-driven show.
Creating Hierarchic Template Sets
An administrator applies the hierarchic approach by selecting check-box Base on original when copying a template set in AVAutomation.
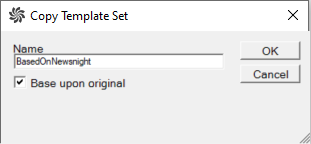
Note: If the Base on original check-box is not selected a physical copy of the entire template set including all nested templates, is created.
Templates are created and customized during the 'show design' phase of a Viz Mosart system setup. This is an advanced task, described in the Template Editor section of AV Automation, in the Viz Mosart Administrator Guide.
Definitions
Some common terminology used in template design and execution:
-
Template type. Denotes the template type or category. Viz Mosart has a predefined set of template types. Each are displayed distinctly in Viz Mosart.
Examples of template types are CAMERA, PACKAGE, VOICEOVER, LIVE, GRAPHIC and DVE -
Template variant. Textual identification of a template for given template type. The combination of template type + template variant identifies a unique template within a template set.
-
Template set. All Viz Mosart templates are located in a template set. A template is uniquely defined by its type and variant name within its corresponding template set. There may exist multiple versions of the same template but in different template sets.
-
Directtakes. A special template set. The templates in this set are intended to be executed in an ad-hoc fashion.
-
Current template set. The current or active template set in Viz Mosart. Changing the current template set is normally done from one of the following places:
-
The Viz Mosart client, using the Studio setups menu
-
The NCS (for example, ENPS) using the Viz Mosart control command [STUDIO SETUP]
-
The Viz Mosart server application AvAutomation, using the the Studio setups menu.
-
-
Shared template set. This is a template set that is shared among all Viz Mosart installations connected to the same Viz Mosart template database.
-
Base template set. The start point for a show design. For example, if a template set TS2 is based upon template set TS1 then TS1 is defined as the base template set of TS2. The following may be used as a short notation: TS2 > TS1
-
Stand alone template set. This is a template set that is not based upon another template set. All template sets in a current installation of Viz Mosart are classified as ‘stand alone’. The following may be used as a short notation for a stand alone template set: TS1 > ()
-
Inherited template set. This is a template set that is based upon another. I.e. if TS2 > TS1 then TS2 is classified as an inherited template set.
-
Template description. Denotes template properties that are common for all Viz Mosart installations in a shared template set. This is used to uniquely identify and describe the template.
-
Template implementation. Contains the behavior or device control aspects of the template. The template implementation is related to the Viz Mosart installation. For a shared template set, each Viz Mosart installation will implement the template set differently, according to local studio setup.
-
Empty template. Denotes a template without implementation. An empty template does nothing when executed. Note that empty templates are not displayed in the Viz Mosart client.
-
Missing template. A template that does not exist in the current template set. A missing template is displayed in Viz Mosart, alerting the operator with red text.
-
Gallery. Typically a single Viz Mosart server, its utilities and the Viz Mosart UI, relates to a dedicated gallery. So a gallery is synonymous with a Viz Mosart installation.
-
Show design. The background task of creating a set of templates, in a logical and programmatically valid order, for controlling a scheduled, rundown-driven, studio transmission.